Authentication is the the process of verifying the credentials a user provides with those stored in a system to prove the user is who they say they are. If the credentials match, then you grant access. If not, you deny it.
This is often used as the authentication process for lower risk systems. You only need a single factor to authenticate, with the most common being a password, so it's more vulnerable to phishing attacks and key loggers.
Single-factor authentication is the simplest way of authentication. It just needs a username and password to allows a user to access a system.
As per the name, it is two-level security; hence it needs two-step verification to authenticate a user. It does not require only a username and password but also needs the unique information that only the particular user knows, such as first school name, a favorite destination. Apart from this, it can also verify the user by sending the OTP or a unique link on the user's registered number or email address.
This is the most secure and advanced level of authorization. It requires two or more than two levels of security from different and independent categories. This type of authentication is usually used in financial organizations, banks, and law enforcement agencies. This ensures to eliminate any data exposer from the third party or hackers.
Going one step further to make your authentication process even more secure is having 3 or more factors. This form of authentication usually works on the premise of:
✳️ something you know (username + password or a username + security question and answer)
✳️ something you have (mobile phone sms, authenticator app, USB key)
✳️ something you are (like a fingerprint / face recognition)
✳️ For these reasons, multi-factor authentication offers the most protection, as you would need to compromise multiple factors, and these factors are a lot more difficult to "hack" or replicate.
It is the simplest way of authentication. It requires the password for the particular username. If the password matches with the username and both details match the system's database, the user will be successfully authenticated.
In this technique, the user doesn't need any password; instead, he gets an OTP (One-time password) or link on his registered mobile number or phone number. It can also be said OTP-based authentication.
2FA/MFA or 2-factor authentication/Multi-factor authentication is the higher level of authentication. It requires additional PIN or security questions so that it can authenticate the user.
Single Sign-on or SSO is a way to enable access to multiple applications with a single set of credentials. It allows the user to sign-in once, and it will automatically be signed in to all other web apps from the same centralized directory.
Social authentication does not require additional security; instead, it verifies the user with the existing credentials for the available social network.
This question comes up at many security architecture meetings, and the answer is "it depends".
It is not unusual for companies to combine various authentication methods to increase security based on the nature of application.
For example, take a banking app. It contains very sensitive information, and could have a huge financial and reputational impacts should it be obtained by the wrong person. The bank may combine personal questions to be answered, along with a customer number and complex password.
On the other hand, for a social media site, you might only require a username and password, which is then checked and verified before allowing access.
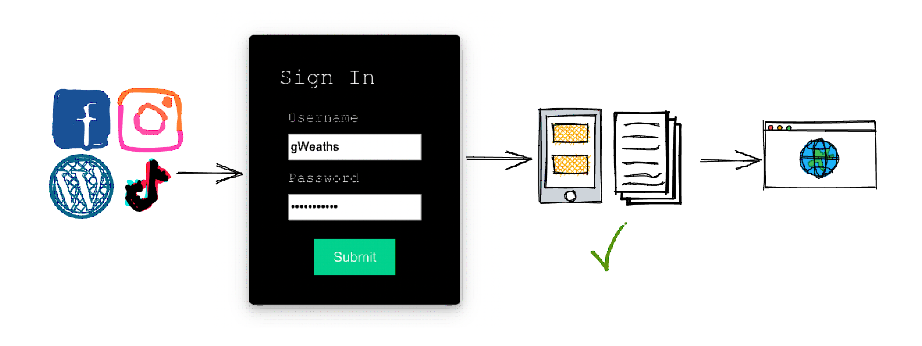
Let's take an example of a social media account. You choose your favorite social media site (which is hosted on a server). The server will ask you to provide credentials to access the site via a sign in page. Here you would type in your username and password that you used when creating the account.
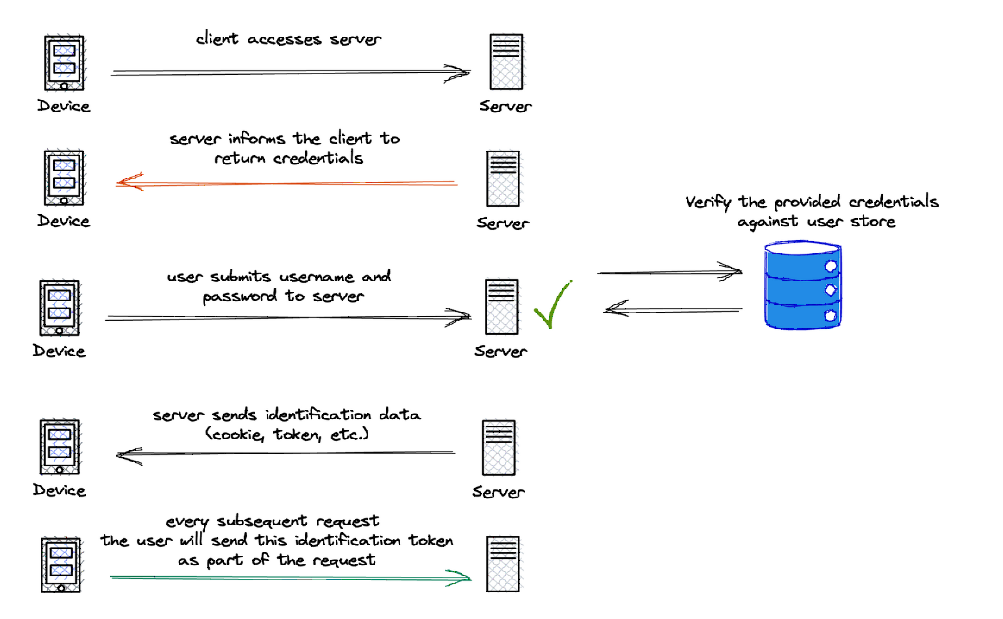
These details are then sent to the server, and the authentication process begins. The details you provided are verified and checked in the server's database, and if they match the details on record you are authenticated.
Authorization is a process by which a server determines if the client has permission to use a resource or access a file.
Authorization is usually coupled with authentication so that the server has some concept of who the client is that is requesting access.
1️⃣ Giving someone permission to download a particular file on a server or providing individual users with administrative access to an application are good examples of authorization.
2️⃣ In secure environments, authorization must always follow authentication. Users should first prove that their identities are genuine before an organization’s administrators grant them access to the requested resources.
3️⃣ Authorization is the process of granting someone to do something. It means it a way to check if the user has permission to use a resource or not.
4️⃣ It defines that what data and information one user can access. It is also said as AuthZ.
5️⃣ The authorization usually works with authentication so that the system could know who is accessing the information.
6️⃣ Authorization is not always necessary to access information available over the internet. Some data available over the internet can be accessed without any authorization, such as you can read about any technology from here.
Authorization can either grant or deny permission to carry out tasks, or access areas of an application.
Let's look at an example:
We've gained access to the social media site, but what we're allowed to do there depends on what we're authorized to to do.
If we try to access someone's profile that we're not friends with (they've not accepted our connection request), we're not authorized to view their profile. This means that we are denied permission to view their shared posts.
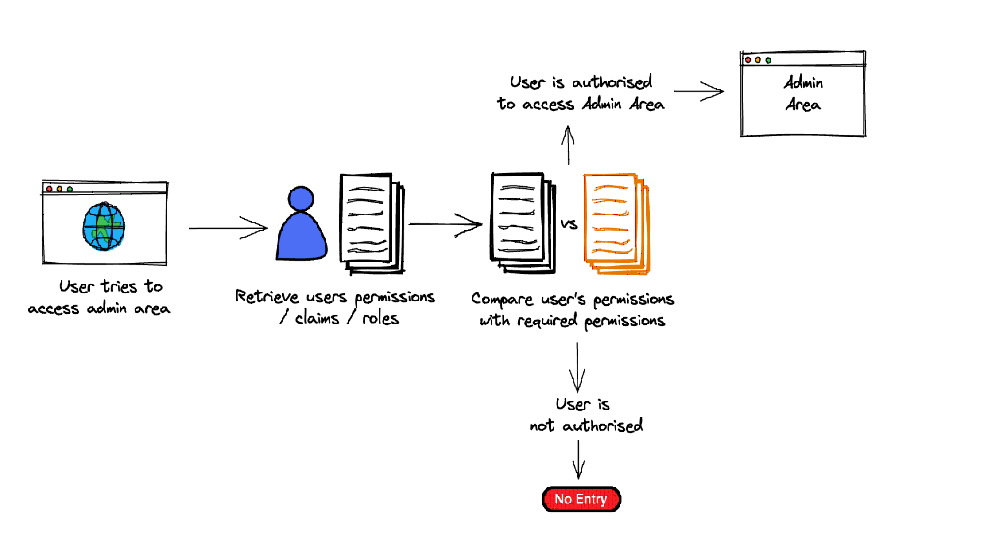
RBAC or Role-based access control technique is given to users as per their role or profile in the organization. It can be implemented for system-system or user-to-system.
JSON web token or JWT is an open standard used to securely transmit the data between the parties in the form of the JSON object. The users are verified and authorized using the private/public key pair.
SAML stands for Security Assertion Markup Language. It is an open standard that provides authorization credentials to service providers. These credentials are exchanged through digitally signed XML documents.
It helps the clients to verify the identity of end-users on the basis of authentication.
OAuth is an authorization protocol, which enables the API to authenticate and access the requested resources.
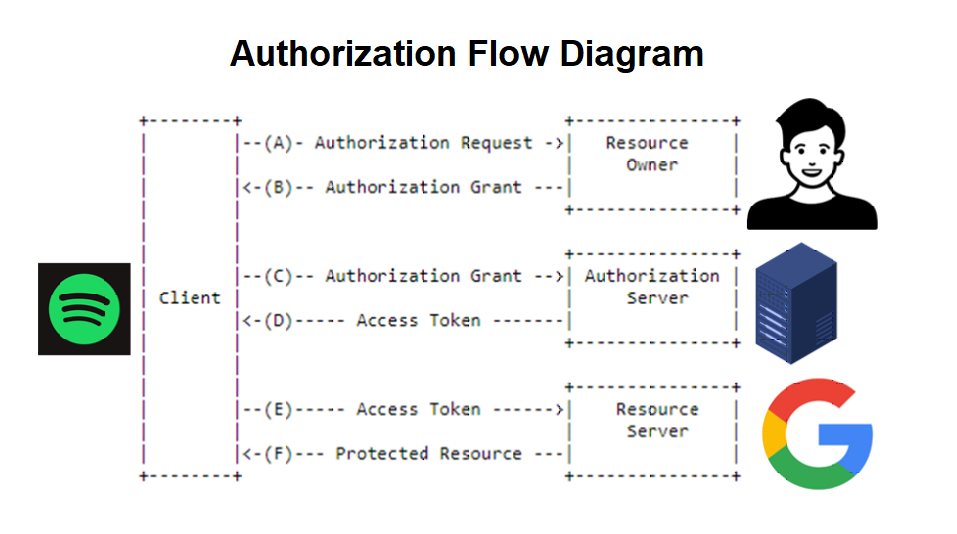
So now that we have a better understanding of the terms, let's look at a scenario you may be familiar with that involves both processes.
At a dinner party with an exclusive guest list, each guest is given a nickname and a secret password.
Upon arrival, a security guard asks you for your nickname and secret password. They then authenticate your credentials against the list they have. If your credentials match, you are handed an envelope showing you've been allowed in.
Once inside you are allowed to access the party and public areas of the venue as these require no authorization (everyone has the permission to enjoy the party). However, you then want to visit the VIP area.
As you approach, another security personnel asks to open your envelope (your permissions and roles). They take a look but unfortunately you do not have the VIP role, and therefore are not authorized to access.Put as simply as possible, authentication verifies the identity of a user or service allowing access, whereas authorization determines what they can do once they're in.
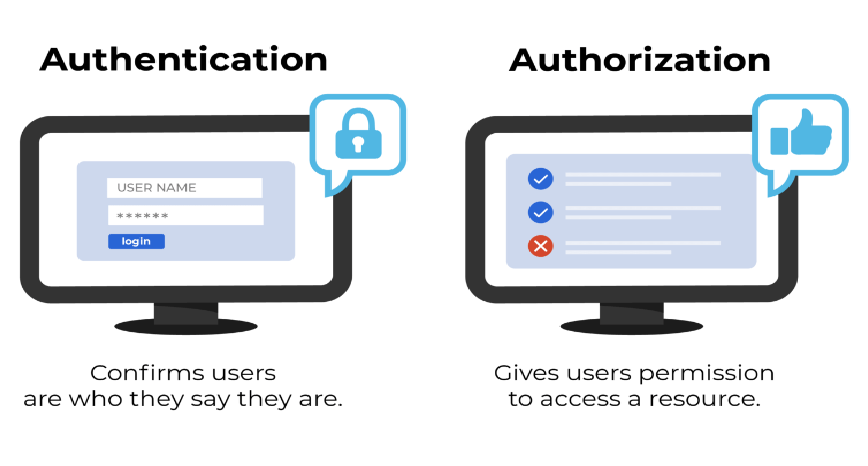
In short, access to a resource is protected by both authentication and authorization. If you can't prove your identity, you won't be allowed into a resource. And even if you can prove your identity, if you are not authorized for that resource, you will still be denied access.
As you can see, although authentication and authorization are very different, each plays an integral part in the security and integrity of the application or system.
These processes go hand in hand, and without one the other is kind of meaningless. If you can gain access to the Admin area, but do whatever you want once in there, it could lead to big problems.
On the other hand, you can't authorize individuals without knowing who they are! Which is why authentication always comes before authorization.
I hope this has been insightful and you now have a clearer understanding of the differences between Authorization and Authentication, and how to use them.
Authenticate = Verifies the identity of a user or process.
Authorize = Determines if the user / system has permission to use a resource or carry out an action.